Why and How to Measure Sulfur in Petroleum Products and Gasoline
ASI Standards ensures the precise analysis of sulfur concentrations in refineries, pipelines, tank terminals, and contract laboratories with certified reference materials and calibration standards.
ASI Standards provides certified reference materials and calibration standards for sulfur determination in petroleum-based fuels by WD-XRF, ED-XRF, and combustion analysis.
Certified reference materials and calibration standards ensure precision in sulfur determination for petroleum fuel analysis.
How Sulfur Affects Fuel Quality
High sulfur in crude lowers the value of the oil. Crude with high sulfur levels is called sour crude. The highest quality crude is called sweet crude, and it has low sulfur content.
How Does Sulfur End Up in Petroleum Products?
Sulfur is naturally present in crude oil at levels ranging from 0.4% to 5%, and companies must remove it during the refining process.
Understand the Dangers of High Levels of Sulfur Oxides
- In humans, high levels of sulfur are linked to asthma, pulmonary, cardiovascular, and respiratory diseases.
- Sulfur affects the environment and causes acid rain, which kills vegetation.
- Sulfur also contributes to particulate matter pollution.
Government Regulations on Sulfur
Because of the risks of high levels of sulfur, governments around the world have instituted regulations on it.
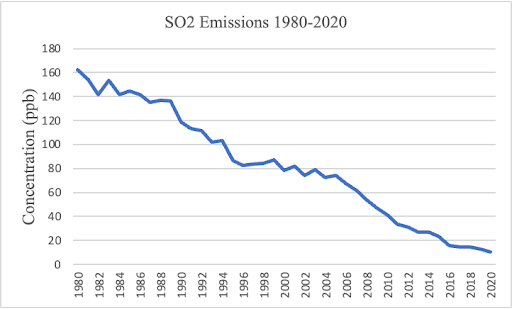
- The Clean Air Act Title IV, also called the Acid Rain Program, aims to reduce SO2 in the atmosphere. Its goal is to cut SO2 emissions by 50%.
- EPA Tier 3 Gasoline Sulfur Standards have reduced sulfur emissions in vehicles by over 97% since its introduction.
- Euro 5 and 6 regulate vehicle engine emissions.
- IMO 2020 reduced allowable sulfur present in ship fuel oil from 3.5% m/m to 0.5% m/m when operating outside of designated emission control zones. Within these zones the allowable sulfur in ship fuel decreases to 0.1% m/m, adhering to Annex VI of the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships. It resulted in a decrease in ship sulfur emissions by 77%.
Reducing sulfur oxides is estimated to have avoided over 570,000 premature deaths worldwide between 2020-2025.
Who Needs to Test for Sulfur in Petroleum Products?
- Refineries
- Contract laboratories
- Tank terminal operators
- XRF, AAS and combustion analyzer instrument manufacturers
International Petroleum Products and Gasoline Sulfur Standards
International standardization bodies such as the ASTM and ISO have developed standards to assist companies in complying with government regulations.
When measuring sulfur concentrations above 20 ppm, XRF is the preferred method because of its quick analysis time and ease of sample preparation.
WD-XRF is the better choice when precise analysis is required, for example, ASTM D2622, ASTM D7039 and ISO 20884.
ED-XRF is best for quick and easy analysis, for example ASTM D4294, ASTM D7220 and IP336.
When measuring for very low levels of sulfur, a different method such as combustion analysis is best due to its increased sensitivity. This includes standards such as ASTM D5453, ASTM D3120 and ISO 20846.
All published ASTM and ISO methods for determining sulfur concentrations in petroleum fuels call for the use of calibration standards. You also need quality control check standards to validate the results.
Preparing Standards and Matrix Matching in Petroleum Products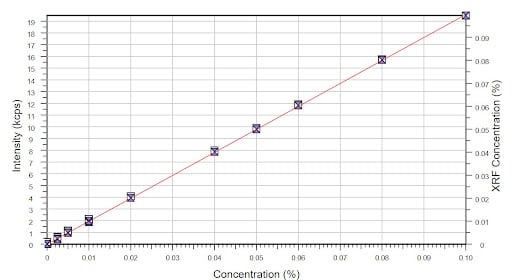
You need calibration because analytical methods such as XRF and combustion analysis are comparative methods. This means that you need calibration with a known concentration sample to compare against the sample of interest.
When making calibration standards to measure sulfur in petroleum products, mineral oil is often the matrix of choice and is the preferred method by ASTM standards.
When you require precise analysis, you need matrix-matched certified reference materials. Matrix-matched standards prevent inaccurate results from C/H ratio interference and heteroatom interference disrupting sulfur measurement. High levels of oxygen in the matrix can disrupt the measurement of sulfur because oxygen absorbs Ka radiation from the X-ray, interfering with sulfur.
For example, if measuring for sulfur on crude oil, you would want to choose crude oil as a matrix rather than mineral oil for precise analysis.
It's also important for calibration standards and reference materials to be homogeneous and stable on the lab shelf.
Find High-Quality Sulfur Standards
ASI Standards is an ISO 9001 accredited laboratory, and all of our sulfur standards are ISO 17034 certified.
We offer sulfur standards in concentrations ranging from sub-ppm to high weight percentage.
They're highly customizable for your particular application.
We sell full calibration standard sets and also conduct quality control on standards for daily use.
We offer sulfur certified reference materials in any matrix including mineral oil, crude oil, residual oil, gasoline, diesel, toluene, xylenes, isooctane, waste oil, ethanol, and marine diesel.
Our standards are NIST traceable and have a two-year shelf life.
Plus, you can rely on speedy delivery, and we need less than a 10-day lead time.
|
Method |
Description |
Sulfur Detection Limits |
Instrumentation |
|
ASTM D2622 |
Sulfur in Petroleum Products |
3 mg/kg to 4.6% weight |
WD-XRF |
|
ASTM D4294 |
Sulfur in Petroleum and Petroleum Products |
0.0150 to 5.00 mass % |
ED-XRF |
|
ASTM D7039 |
Sulfur in Gasoline, Diesel Fuel, Jet Fuel, Kerosine, Biodiesel, Biodiesel Blends, and Gasoline-Ethanol Blends |
3.2 mg/kg to 2822 mg/kg |
WD-XRF |
|
ASTM D7220 |
Sulfur in Automotive, Heating, and Jet Fuels |
3 mg/kg to 942 mg/kg. |
Monochromatic ED-XRF |
|
ASTM D3120 |
Trace Quantities of Sulfur in Light Liquid Petroleum Hydrocarbons |
3.0 mg/kg to 1000 mg/kg |
Oxidative Microcoulometry |
|
ASTM D5453 |
Determination of Total Sulfur in Light Hydrocarbons, Spark Ignition Engine Fuel, Diesel Engine Fuel, and Engine Oil |
1.0 mg/kg to 8000 mg/kg |
Ultraviolet Fluorescence |
|
ASTM D7183 |
Total Sulfur in Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals |
0.1mg/kg to 10 mg/kg |
Ultraviolet Fluorescence |
|
IP 336 |
Determination of sulfur content |
0.03 % (m/m) to 5 % (m/m) |
ED-XRF |
|
IP 490 |
Determination of sulfur content of automotive fuels |
3 mg/kg to 500 mg/kg, |
Ultraviolet Fluorescence |
|
ISO 20846 |
Determination of sulfur content of automotive fuels |
3 mg/kg to 500 mg/kg |
Ultraviolet Fluorescence |
|
ISO 20884 |
Determination of sulfur content of automotive fuels |
5 mg/kg to 500 mg/kg |
WD-XRF |
|
ISO 8754 |
Determination of sulfur content |
0.03 % (by mass) to 5.00 % (by mass) |
ED-XRF |
|
ISO 14596 |
Determination of sulfur content |
0.001 % (m/m) to 2.50 % (m/m) |
WD-XRF |
|
ISO 13032 |
Determination of low concentration of sulfur in automotive fuels |
8 mg/kg to 50 mg/kg |
ED-XRF |
Talk to our team about purchasing sulfur in crude oil standards or having custom standards created for your application.